5.8 Compare the package name lengths with download counts
Here, we still focused on all of R-packages on CRAN, and made comparison between their name lengths and total downloads over the most recent 6 month period.
Finding 1: The name lengths of R-packages have no significant correlation with total downloads, over the most recent 6 month period.
We could see from Figure 5.22 that, the influence on download volume resulted from name length is not obvious. But we could still observe that the name lengths of most of R-packages are centered before 10 characters long. The names , with more than 6,000,000 downloads, are between 5 and 9 characters long. The most downloaded one is R-package rlang whose name length is 5.
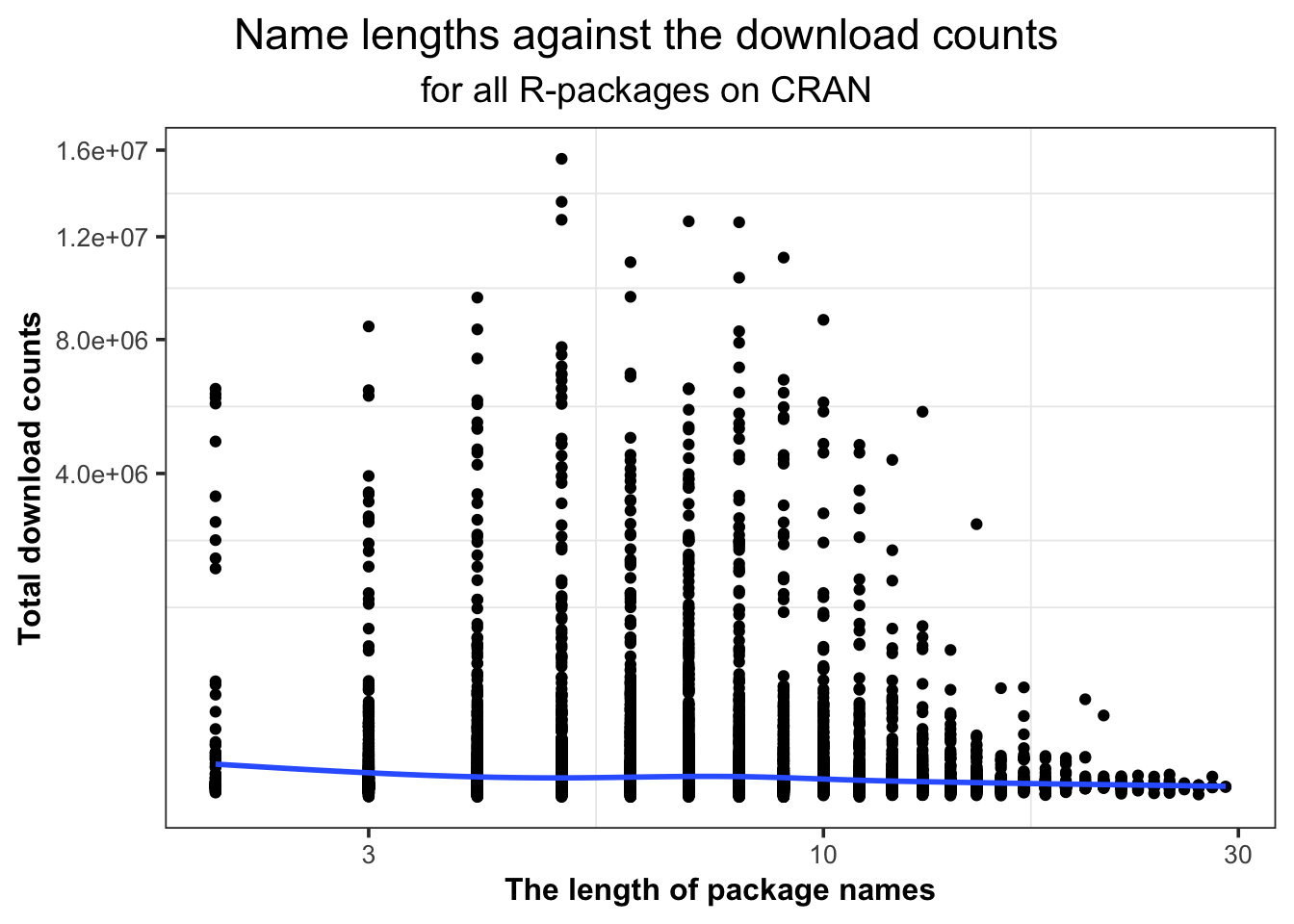
Figure 5.22: The names of R-packages with more than 6,000,000 downloads are between 5 and 9 characters long.
Finding 2: The average name length of R-packages is about 7.8 characters long, and over half of the R-packages tend to have shorter names, which may make it more easier to be remembered by users.
Table 5.19 shows that the average name length of all the R-packages is 7.8472034. And over half of the CRAN R-packages are more likely with name lengths below average. And R-packages with shorter names can be easier to get relatively higher downloads. That may because shorter named packages are easier for users to remember.
| number of short names | percentage of short names | total average name length |
|---|---|---|
| 9289 | 52.58718 | 7.847203 |
After finding that there is no obvious relationship between the name lengths and the download volume, a new question came up : Can the name lengths of the R-packages be linked to the time of initial release date?
Finding 4: For task view R-packages, the name lengths increase with the initial release dates, especially for Bayesian packages.
We may have this kind of experience in life : for example, detective novels, the later they are released, the less names can be chosen, because many names have been occupied by the books published earlier, with the same theme. Therefore, those later published books often have to lengthen their names to distinguish themselves from the existing books. Coincidentally, we guessed the naming of R-packages from the same topic would also be correlated to the initial release time. So, we looked back to the CRAN task view R-packages(“CRAN Task Views,” n.d.), for conducting comparison among R-packages from the same topic. Figure 5.23 shows the name lengths of CRAN task view R-packages against the initial release dates. It is obvious that the name lengths of task view R-package tend to increase with the initial release dates, especially for Bayesian R-packages.
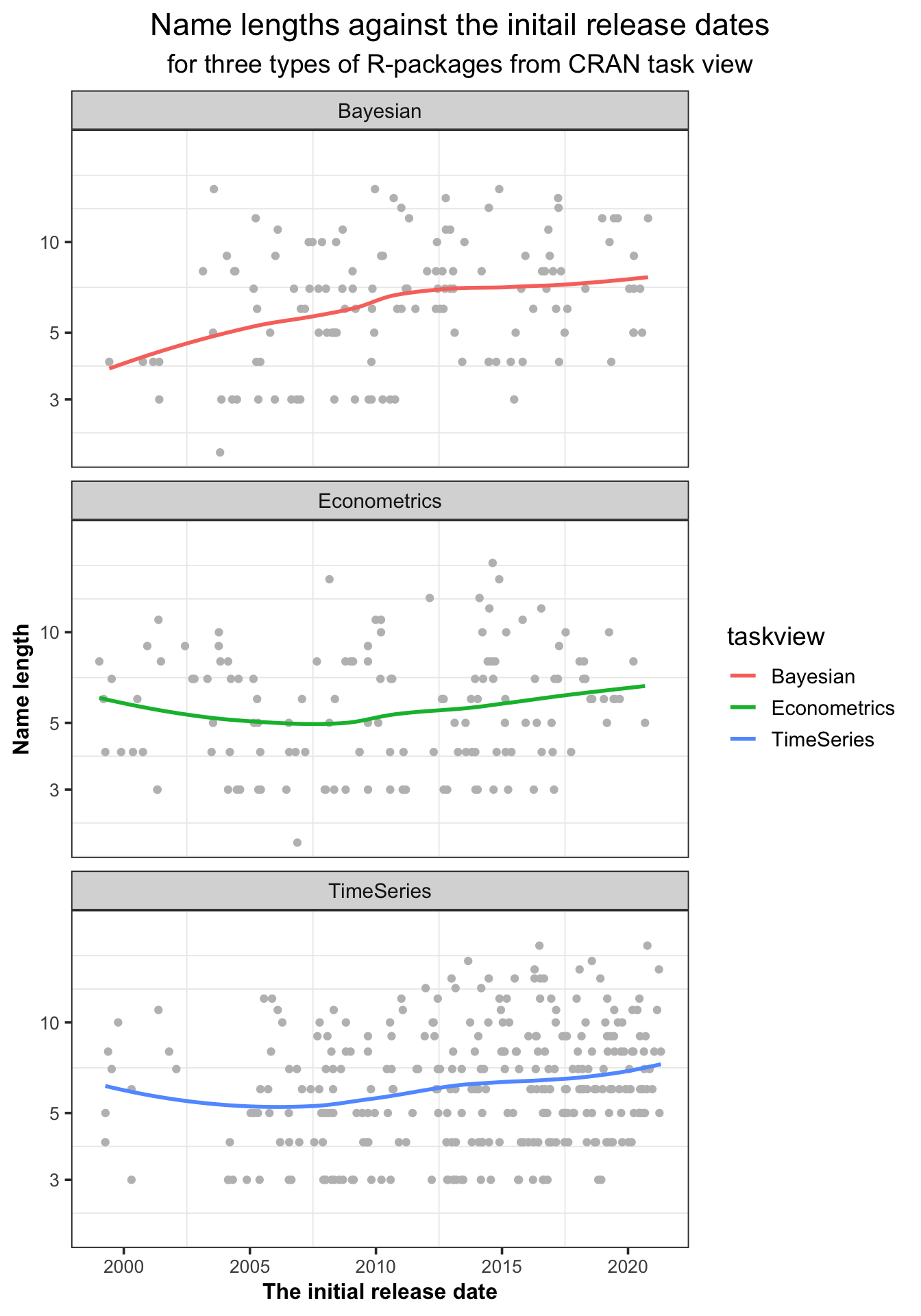
Figure 5.23: The name lengths of task view R-packages slightly increase with the initial release dates.
Finding 5: For all of R-packages on CRAN, the average name length tends to generally increase with the initial release date.
Although we’d better explore this question among R-packages within the same topic, we also had a view on the annual change in the average name length, for all of R-packages on CRAN.
Figure 5.24 shows the average name length for all of R-packages on CRAN, released in each year. It is obvious that the name lengths of those R-packages generally increase year by year.
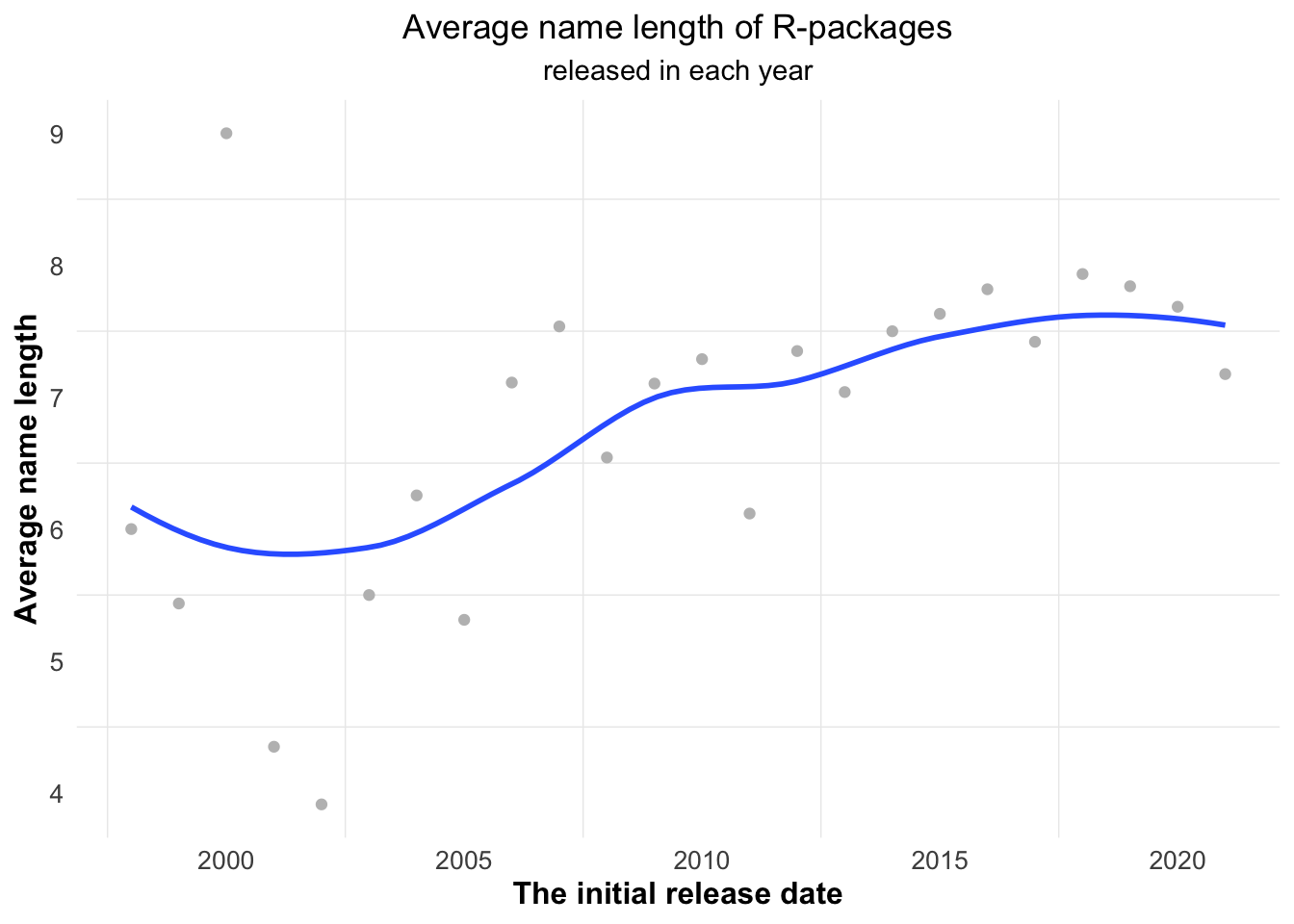
Figure 5.24: The average name length for all of R-packages on CRAN released in each year, tends to rise along the time.